What Is The Use Of Calorimeter, Certain instruments stand out in the world of scientific investigation due to their versatility and importance in a variety of sectors. Among these, the calorimeter stands out, providing crucial insights on the transfer of energy in many processes. If you’ve ever wondered what calorimeters are used for and how they fit into scientific study, you’ve come to the correct place. In this comprehensive tutorial, we’ll go deep into the realm of calorimeters, investigating their uses and highlighting their significance in both academic and practical settings.
What Is The Use Of Calorimeter
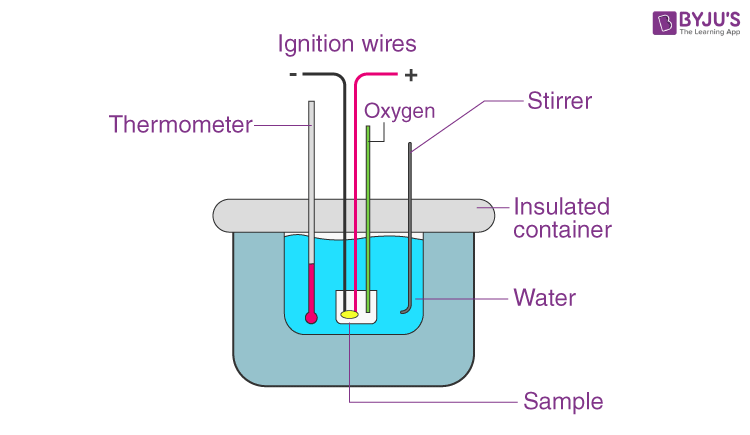
What is a calorimeter?
Before we get into its applications, let’s define what a calorimeter is. Simply described, a calorimeter is a device that measures the amount of heat produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction or physical process. Calorimeters are essential for studying the thermodynamic properties of substances and reactions because they properly quantify these heat changes.
Types of Calorimeters
Calorimeters come in a variety of configurations, each adapted to a specific application. Some typical categories are:
A bomb calorimeter, which is mostly used in chemistry and food science, is designed to determine a sample’s heat of combustion by burning it in a sealed chamber filled with oxygen.
Coffee cup calorimeters, also known as constant-pressure calorimeters, are simple devices used in educational settings to measure the heat exchanged during chemical reactions that take place under constant pressure.
Differential Scanning Calorimeters (DSCs) are widely used in materials science and pharmaceutical research. They detect the heat flow into or out of a sample while it is subjected to regulated temperature changes, providing information about phase transitions, purity, and thermal stability.
Adiabatic Calorimeter: These calorimeters are designed to reduce heat exchange with the environment, enabling for exact measurements of heat changes in highly exothermic or endothermic reactions.
Uses for Calorimeters
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals, let’s look at the wide range of applications in which calorimeters play an important role:
Calorimeters are commonly used in energy research to calculate the calorific value of fuels, which represents the amount of energy released during burning. This knowledge is critical for determining the efficiency of different fuels and optimizing energy production operations.
In nutrition research, calorimeters are used to determine the energy content of various foods. Researchers can measure the calorie content of a food sample by burning it in a bomb calorimeter and monitoring the heat emitted, which helps with dietary assessment and formulation.
Enzyme activity can be studied using calorimeters, which measure heat changes during substrate conversion. This allows researchers to better understand enzyme kinetics, substrate specificity, and the effects of inhibitors on enzymatic activity.
Calorimeters offer useful data for investigating thermodynamic parameters like enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy. Researchers can learn about the basic principles that regulate chemical and physical processes by measuring heat fluctuations under various settings.
Calorimeters are essential for measuring heat changes in chemical reactions, including synthesis and complex metabolic pathways. This enables researchers to adjust reaction settings, evaluate reaction kinetics, and discover potential side reactions or byproducts.
Calorimeters are used in pharmaceutical quality control to ensure medication formulation stability and purity. Differential scanning calorimetry, in particular, is useful for determining the thermal behavior of medicinal substances and finding unwanted interactions or degradation.
Calorimeters are used in materials science to determine the thermal characteristics of materials such as polymers, metals, and ceramics. Heat flow and phase transitions can be studied to optimize material synthesis, assess thermal stability, and forecast material behavior under various situations.
Finally, calorimeters are vital tools used in a wide range of scientific areas, including chemistry, physics, food science, and materials engineering. Calorimeters, by correctly quantifying heat changes in various processes, provide essential insights into the fundamental mechanisms driving energy transmission and transformation.
Also Read:- What Is Placenta Class 12
Calorimeters have a wide range of applications, including estimating the calorific value of fuels, investigating enzyme kinetics, and characterizing materials. As scientific study advances, calorimeters continue to play an unequaled role in revealing the mysteries of the physical and chemical worlds.
So, the next time you see a calorimeter in a lab or read about its applications in scientific literature, consider how profoundly this basic device has influenced our knowledge of energy, matter, and the fundamental processes that control our universe.

